Among the types of clamps used in high-voltage overhead lines, straight boat-type clamps and crimped tension-resistant tube-type
tension clamps are more common. There are also pre-twisted clamps and wedge-type clamps. Wedge-type clamps are known for
their simplicity. The structure and installation method are recommended by many installation and operation departments. The
pre-twisted cable clamp is the standard cable clamp of OPGW. It is now also called the common backup cable clamp type in the
“three-span” section. Today, let’s take a look at these two The structure and precautions of the seed clamp.
1 wedge clamp
1.1 Usage of wedge clamp
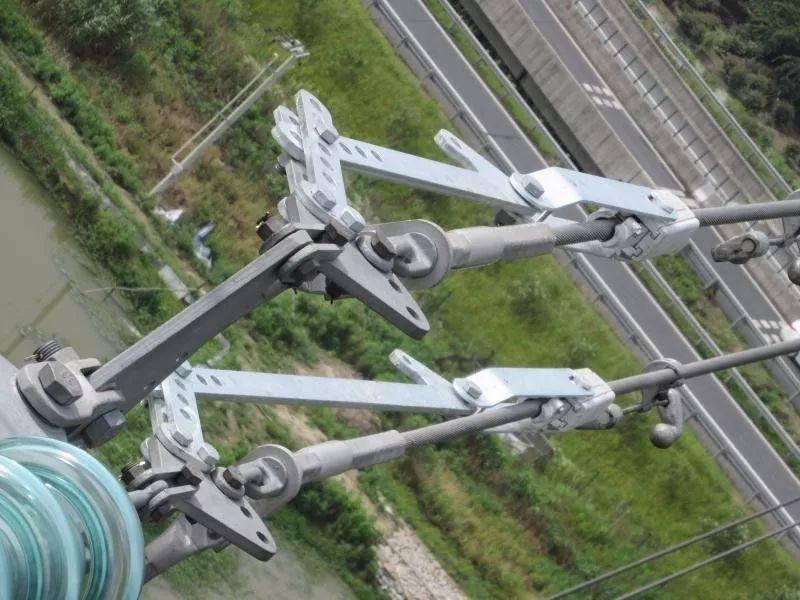
Wedge-type cable clamps can replace common compression and tension-resistant cable clamps, and can also be used as backup
cable clamps, which can be used for ground wires and conductors. Due to structural characteristics, wedge clamps are only used
in tension towers.
1.2 Wedge clamp structure
There is a wedge in the wedge clamp cavity. When the conductor and the clamp are relatively displaced, the conductor, the wedge,
and the clamp cavity are automatically compressed to ensure the clamp’s grip on the conductor. Its structure is shown in Figure 1.
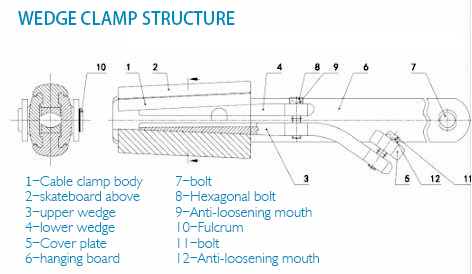
Figure 1 Wedge clamp structure
In Figure 1, 1 is the cable clamp cavity, 3 and 4 are wedges, used to compress the ground wire, and the lower wedge 3 has a tail
leading out. For conventional wedge-type cable clamps, jumpers can be installed here. Wedge-type backup cable clamp, since there
is no need to connect jumpers, there may be no lead-out device here. The disassembly of a wedge-type cable clamp is shown in
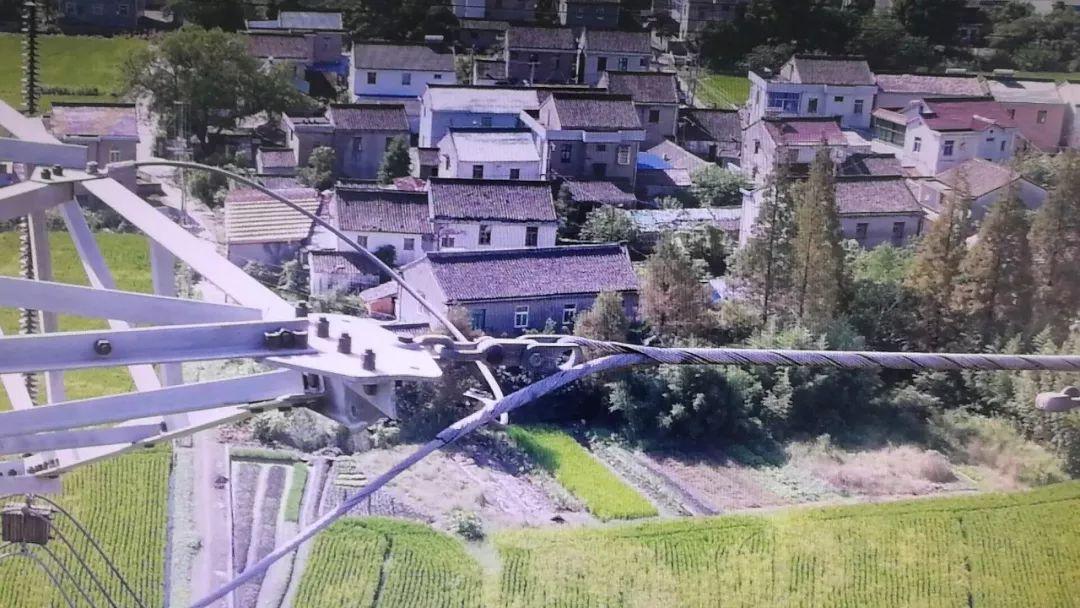
Figure 2, and the on-site installation diagram is shown in Figure 3.
Figure 2 Disassembly of wedge clamp
Figure 3 Wedding wire clip (backup line clip) on -site installation map
2.3 Precautions for wedge-type cable clamps
1) Installation pre-tightening force of wedge-type backup cable clamp
The wedge of the wedge clamp cannot move in the tightening direction, but can move in the opposite direction. If the wedge clamp and
the ground wire are not tightened, the wedge will be slowly sent out under the action of long-term wind vibration. Therefore, pre-tightening
force must be applied when installing the wedge backup cable clamp, and necessary anti-loosening measures must be taken.
2) The position of the anti-vibration hammer after installing the wedge clamp
After the wedge clamp is installed, its fracture will inevitably become a fixed point, so the installation distance of the anti-vibration hammer
should be calculated from the exit of the wedge clamp cavity.
2 pre-twisted wire clips
2.1 Application of pre-twisted wire clamps
OPGW contains communication optical fibers. General crimp-type tension-resistant cable clamps can easily damage the internal optical fiber
during the crimping process. Pre-twisted cable clamps do not have such problems. Therefore, pre-twisted cable clamps were first used in OPGW,
including straight wires. Clamps and tension clamps. With the development of technology, it is gradually used in general lines. In recent years,
the operation department’s attention to three-span has opened up a new use of pre-twisted cable clamps – as backup cable clamps (safety
backup cable clamps) for three-span sections.
2.2 Pre-twisted cable clamp structure
1) Ground wire pre-twisted backup clamp
The purpose of the ground wire backup clamp is to use the backup clamp to provide gripping force to the ground wire when the original tension
clamp outlet of the ground wire is broken (operational statistics show that most of the ground wire breakage occurs at the wire clamp outlet).
Reliably connect with wires to avoid ground wire falling accidents.
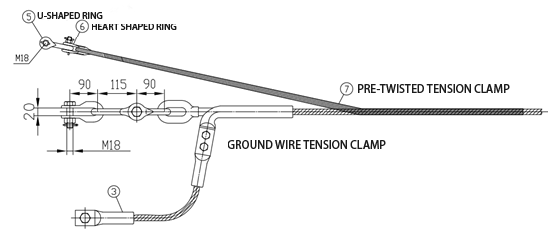
The appearance and structure of the pre-twisted backup cable clamp are shown in Figure 4 and Figure 5. The pre-twisted wire forms an
empty tube, and the inner surface contains sand. During installation, the pre-twisted wire is wrapped around the ground wire, and the pre-twisted
wire compression force and the inner surface are used. The grit on the surface provides grip. According to the size of the on-site ground wire,
the pre-twisted wire of the backup clamp can be divided into 2 layers and 1 layer. The 2-layer structure means that a layer of pre-twisted wire is
installed outside the ground wire, and then a pre-twisted wire with a ring is installed in addition to the pre-twisted wire. The twisted wire clamp has
sand in both layers of pre-twisted wire.
Figure 4 Appearance of pre-twisted cable clamp
Figure 5 Simple installation diagram of pre-twisted cable clamp
2) Pre-twisted OPGW cable clamp
For OPGW, pre-twisted cable clamps are components that bear mechanical tension and can be divided into two types: tensile and straight.
The tensile on-site installation is shown in Figure 6, and the straight on-site installation is shown in Figure 7.
Figure 6 OPGW tension-resistant pre-twisted cable clamp
The main structure of the OPGW tensile-resistant pre-twisted cable clamp is the same as the above-mentioned ground wire pre-twisted
backup cable clamp. The pre-twisted wire and internal sand are in close contact with the OPGW to provide gripping force. It should be
noted that the OPGW tensile-resistant pre-twisted cable clamp The clips all have a 2-layer pre-twisted wire structure. The inner layer of
pre-twisted wire provides protection for the OPGW on the one hand, and on the other hand, the outer layer of pre-twisted wire changes
the shape significantly and ensures sufficient grip strength. In addition, for pole towers that need to be grounded, some pre-twisted tension
clamps are equipped with special drainage wires to ensure that the OPGW is well grounded.
Figure 7 OPGW linear pre-twisted cable clamp
There are two differences between the OPGW linear pre-twisted cable clamp and the tensile strength. First, there is generally no sand
inside the linear pre-twisted cable clamp, because the linear tower does not need to withstand the tensile force of the wire; the second
is the connection between the cable clamp and the tower body. The structure is different and is connected to the tower body through
special expansion protection and hardware.
3) Pre-twisted wire backup clamp
When defects in the original tension clamp occur in the conductor, the pre-twisted backup clamp can be used as a temporary treatment
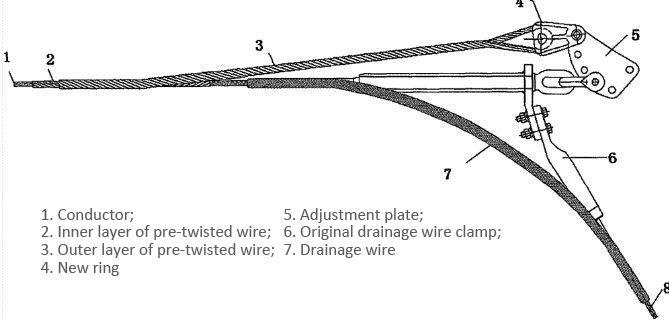
measure to provide sufficient holding force and flow capacity. The structure is shown in Figure 8.
Figure 8 Pre-twisted wire backup clamp
In Figure 8, the pre-twisted wires 2 and 3 are used to connect to the adjustment plate to provide mechanical support, and the drainage
wire 7 is used to connect the wire and the original drainage jumper to achieve flow, thereby avoiding overheating and other defects due
to the position of the tension clamp drainage plate. Affects the flow of wires.
2.3 Precautions for pre-twisted cable clamps
1) The grounding method and internal sand material of the pre-twisted backup cable clamp
There are two types of sand grains inside the pre-twisted wire. One is non-conductive emery. The ground wire-pre-twisted wire interface
formed by the pre-twisted wire clip has relatively poor electrical conductivity and is generally not used in areas where flow may occur.
Another type of sand is conductive sand doped with metal, which has a certain degree of conductivity and is used in working conditions
where flow may occur.
For lines where the ground wire is insulated from tower to tower, in order not to change the original grounding method, the backup wire
clamp is insulated (such as a backup wire clamp with a piece of insulator strung together). The amplitude of the induced current in the
ground wire is very low at ordinary times. When a lightning counterattack occurs, it is generally The lightning energy is discharged through
the gap of the ground wire insulator. At this time, the backup clamp will not bear the flow function, so the sand inside the clamp can be
made of emery.
For lines where ground wires are grounded from tower to tower, the backup wire clips are generally directly grounded to the tower body
through fittings. Normally, the induced current in the line is large, and when a lightning counterattack occurs, current will pass through
the backup wire clips. At this time, conductive wire clamps should be used in the backup wire clips. sand.
For lines with a single-end grounding in the ground wire tension section, the grounding method of the pre-twisted backup clamp is the
same as the grounding method of the original ground wire at the tower location. At the same time, if it is insulated, emery can be used.
The internal part of the directly grounded backup clamp should be Use conductive sand. This is also the grounding method and sand
selection principle of the pre-twisted backup cable clamp.
2) The material combination of the pre-twisted cable clamp and the ground wire
The pre-twisted cable clamp is equivalent to adding a layer of metal protective strip outside the ground wire. If the materials between
the two are not matched well, it will cause electrochemical corrosion problems when the conductivity of rainwater is high. Therefore,
the same material as the ground wire is generally selected as the material of the pre-twisted cable clamp.
3) End treatment of pre-twisted wire
The tail end of the pre-twisted wire should be rounded to avoid corona, and at the same time, the pre-twisted wire should be prevented
from rising and causing poor contact with the ground wire.
Post time: Oct-16-2023